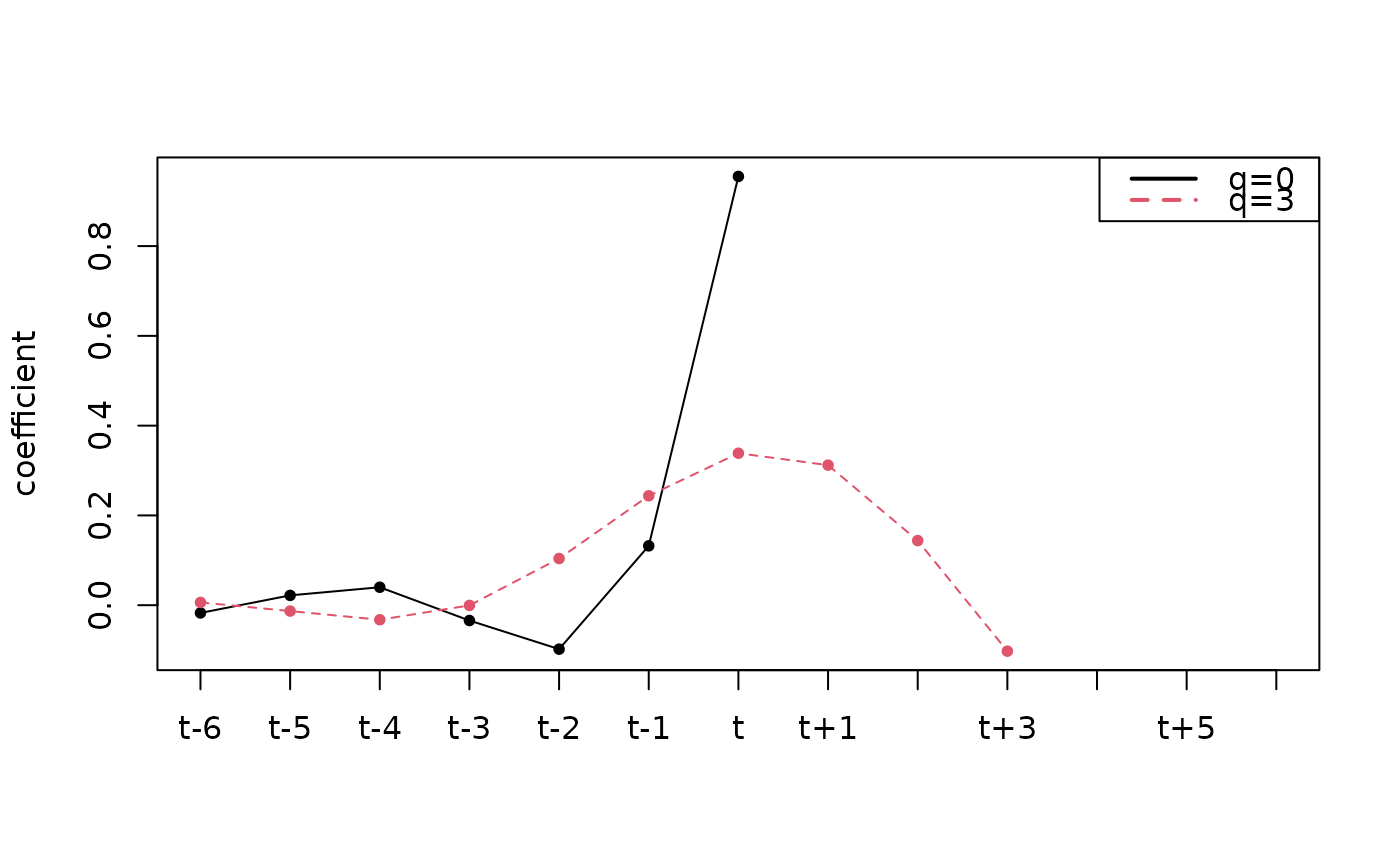
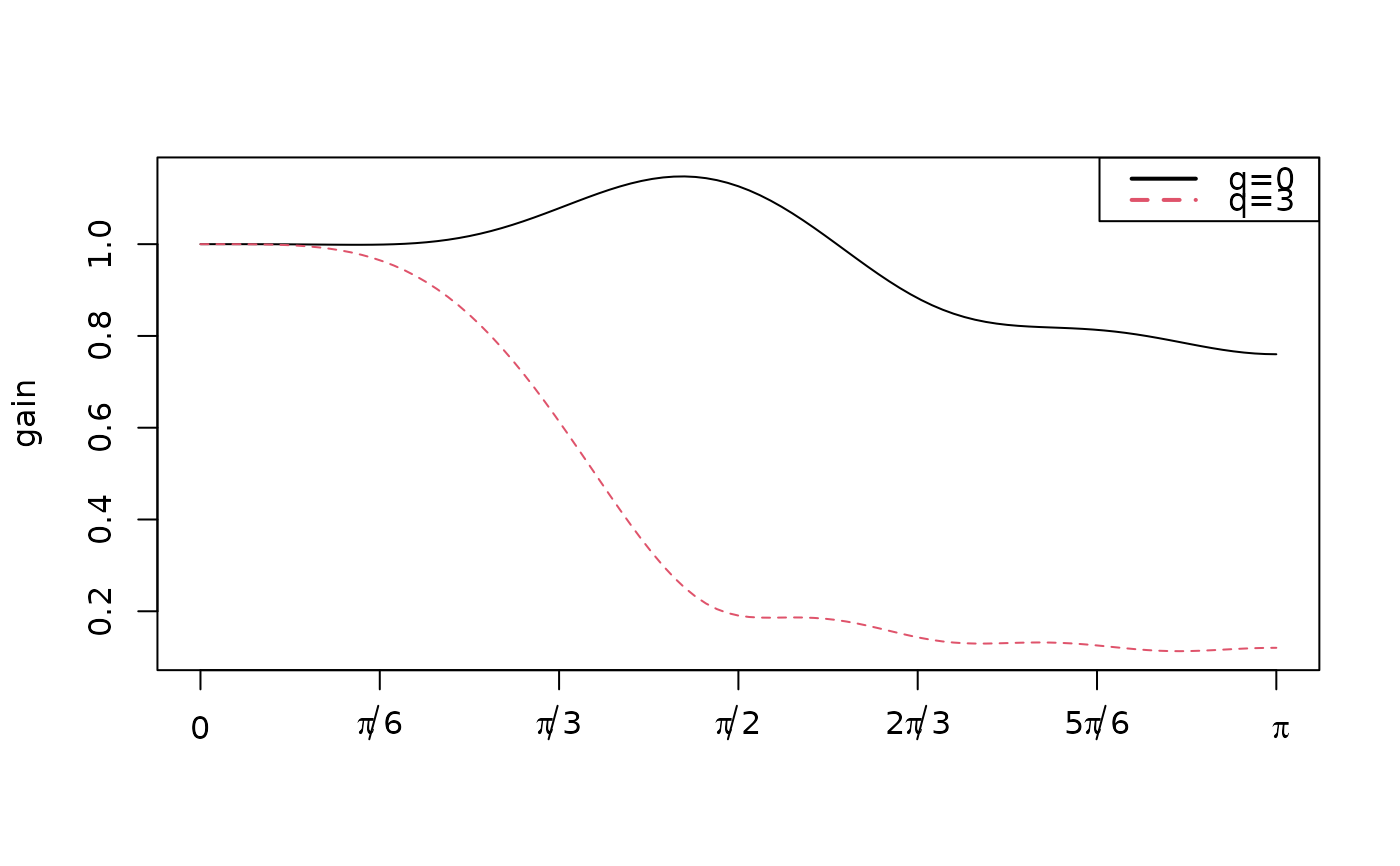
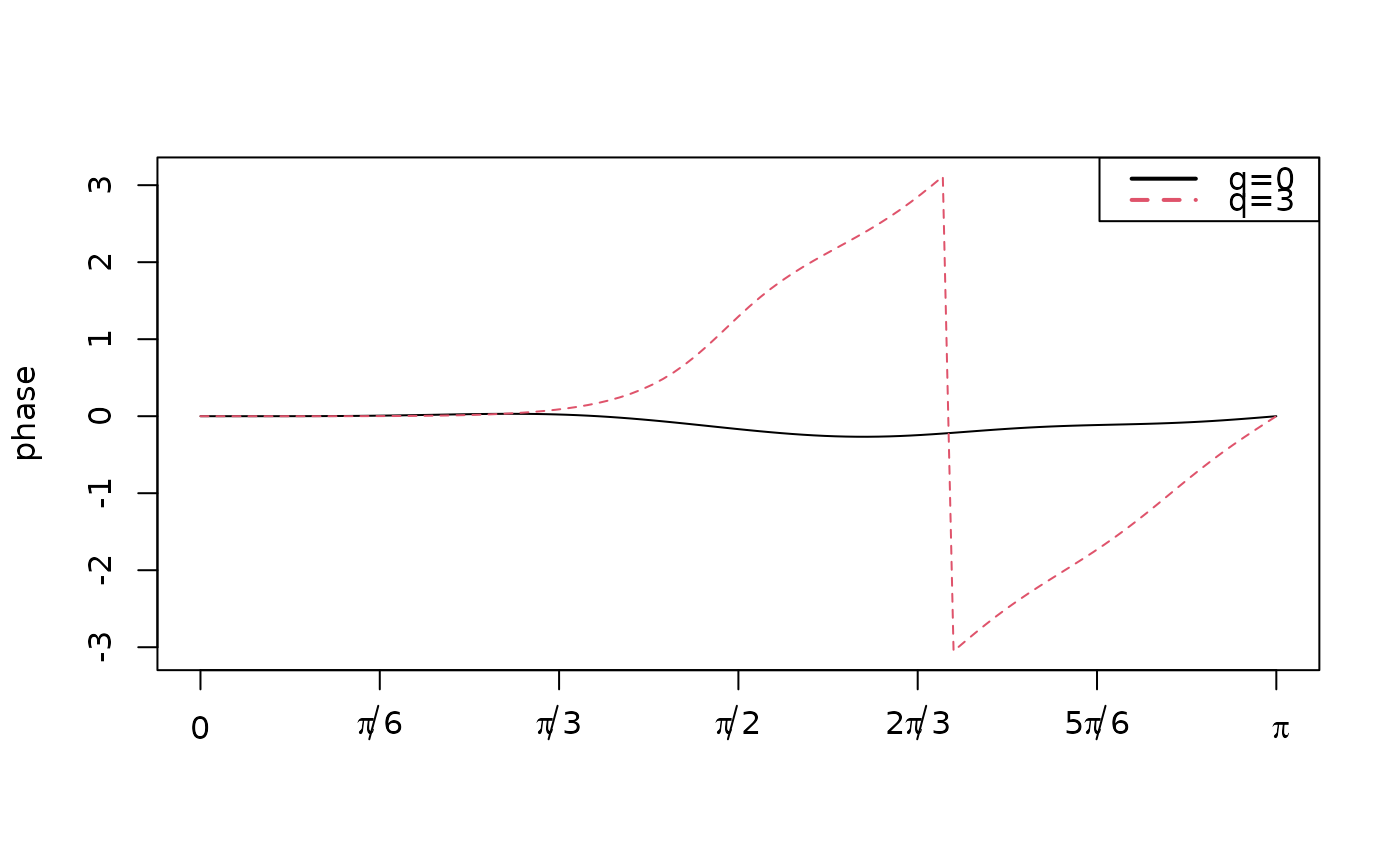
Functions to plot the coefficients, the gain and the phase functions.
Usage
plot_coef(x, nxlab = 7, add = FALSE, ..., xlab = "", ylab = "coefficient")
# Default S3 method
plot_coef(
x,
nxlab = 7,
add = FALSE,
zero_as_na = TRUE,
q = 0,
legend = FALSE,
legend.pos = "topright",
...,
xlab = "",
ylab = "coefficient"
)
# S3 method for class 'moving_average'
plot_coef(x, nxlab = 7, add = FALSE, ..., xlab = "", ylab = "coefficient")
# S3 method for class 'finite_filters'
plot_coef(
x,
nxlab = 7,
add = FALSE,
zero_as_na = TRUE,
q = 0,
legend = length(q) > 1,
legend.pos = "topright",
...,
xlab = "",
ylab = "coefficient"
)
plot_gain(
x,
nxlab = 7,
add = FALSE,
xlim = c(0, pi),
...,
xlab = "",
ylab = "gain"
)
# S3 method for class 'moving_average'
plot_gain(
x,
nxlab = 7,
add = FALSE,
xlim = c(0, pi),
...,
xlab = "",
ylab = "gain"
)
# S3 method for class 'finite_filters'
plot_gain(
x,
nxlab = 7,
add = FALSE,
xlim = c(0, pi),
q = 0,
legend = length(q) > 1,
legend.pos = "topright",
n = 101,
...,
xlab = "",
ylab = "gain"
)
plot_phase(
x,
nxlab = 7,
add = FALSE,
xlim = c(0, pi),
normalized = FALSE,
...,
xlab = "",
ylab = "phase"
)
# S3 method for class 'moving_average'
plot_phase(
x,
nxlab = 7,
add = FALSE,
xlim = c(0, pi),
normalized = FALSE,
...,
xlab = "",
ylab = "phase"
)
# S3 method for class 'finite_filters'
plot_phase(
x,
nxlab = 7,
add = FALSE,
xlim = c(0, pi),
normalized = FALSE,
q = 0,
legend = length(q) > 1,
legend.pos = "topright",
n = 101,
...,
xlab = "",
ylab = "phase"
)Arguments
- x
coefficients, gain or phase.
- nxlab
number of xlab.
- add
boolean indicating if the new plot is added to the previous one.
- ...
other arguments to
matplot.- xlab, ylab
labels of axis.
- zero_as_na
boolean indicating if the trailing zero of the coefficients should be plotted (
FALSE) or removed (TRUE).- q
q.
- legend
boolean indicating if the legend is printed.
- legend.pos
position of the legend.
- xlim
vector containing x limits.
- n
number of points used to plot the functions.
- normalized
boolean indicatif if the phase function is normalized by the frequency.